Manufacturing ERP systems have proven that they can increase efficiency and profitability, whilst increasing quality and output for manufacturing businesses.
ERP system clearly allow manufacturing organisations to do more, with less.
But with so many manufacturing ERP systems and vendors on the market, plus an army of resellers and sytstems integrators pushing different products, with almost no differentiation, it can be hard to know which system to choose for your business.
In this post, we'll cover the best ERP systems for any size of manufacturing organisation, how to compare them and talk about many of the key questions you need to answer before embarking on an ERP implementation project.
Contents
Best Manufacturing ERP Software
1. SAP S/4 HANA
2. Microsoft Dynamics 365
3. Infor CloudSuite Industrial
4. Epicor Kinetic
5. Oracle ERP Cloud
6. IFS Cloud
7. SAP Business One
8. Odoo
9. Microsoft Dynamics Business Central
10. Plex Manufacturing Cloud
Manufacturing ERP FAQ:
What is manufacturing ERP?
How do you compare manufacturing ERP systems?
What are the features of a manufacturing ERP system?
How long does it take to implement a manufacturing ERP?
How much does it cost to implement a manufacturing ERP?
What are the different stages of implementing a manufacturing ERP?
What's the difference between MRP and ERP?
Best Manufacturing ERP of 2024
| Manufacturing ERP: |
Cost: |
Scalability: |
Our Score: |
| SAP S/4 HANA |
High |
100 - 10,000+ employees |
4.5/5 |
| Microsoft Dynamics 365 |
Medium |
100 - 5,000 employees |
3/5 |
| Infor CloudSuite Industrial |
Medium |
100 - 5,000 employees |
4/5 |
| Epicor Kinetic |
Low-Medium |
100 - 1,000 employees |
3/5 |
| Oracle ERP Cloud |
Medium |
100 - 5,000 employees |
3.8/5 |
| IFS |
Medium |
500 - 5,000 employees |
4/5 |
| SAP Business One |
Low |
50 - 500 employees |
3/5 |
| Odoo |
Low |
10 - 500 employees |
3/5 |
| Microsoft Dynamics Business Central |
Low |
50 - 500 employees |
3/5 |
| Plex Manufacturing Cloud |
Low-Medium |
100 - 1000 employees |
3.5/5 |
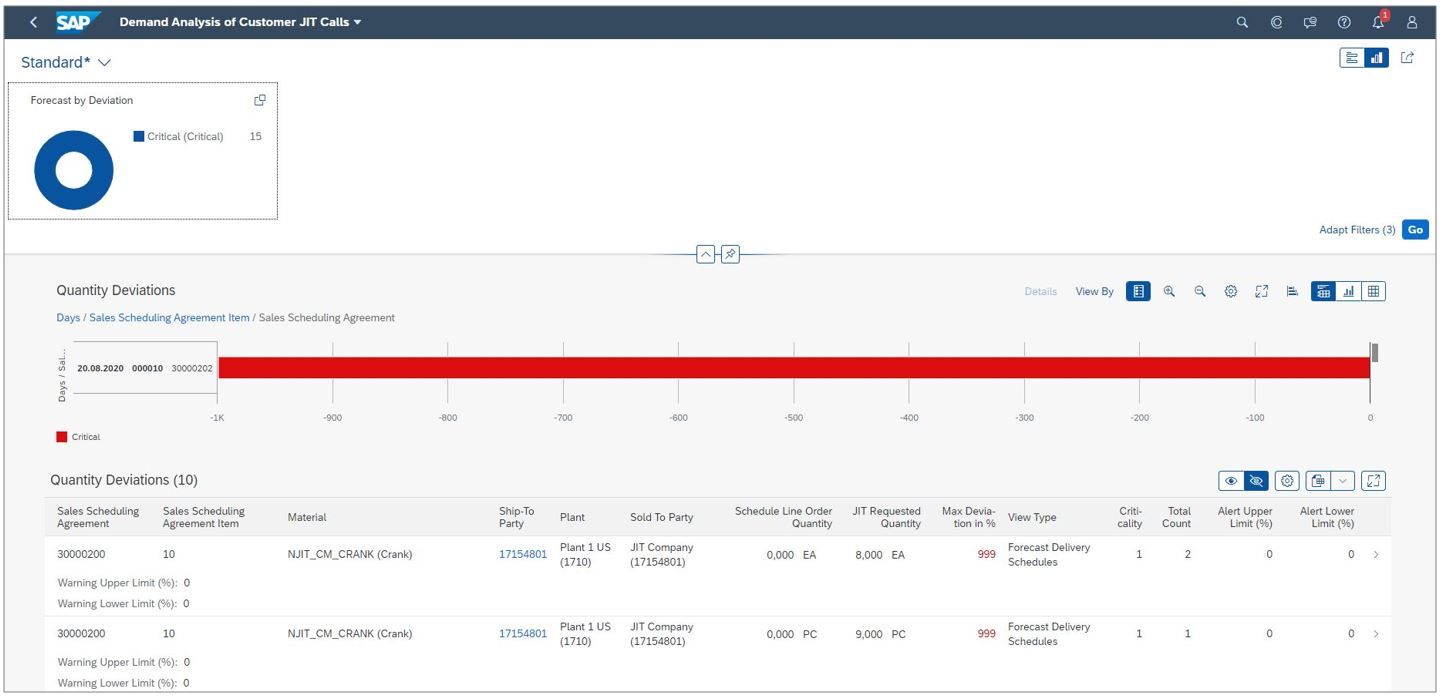
SAP S/4 HANA is one of the best manufacturing ERP systems available on the market in 2024. The system boasts unparalleled scalability, serving fast growing small and medium sized businesses, as well as large enterprises with several thousands of employees.
This manufacturing ERP is available in a number of deployments, from traditional On-Premise or in a Private or Public Cloud environment.
The latest Public Cloud option for S/4 HANA is particularly appealing to small and medium sized manufacturing companies, as it comes out of the box with hundreds of best practice processes that are ready to deploy, reducing the cost and timeline of implementing SAP.
What manufacturing ERP features does SAP S/4 HANA provide?
SAP S/4 HANA supports a variety of manufacturing sub-industries and processes including discrete manufacturing, process manufacturing, make to stock, make to order, engineer to order and configure to order.
Furthermore, S/4 HANA supports:
- (MRP) Material Requirements Planning
- Supply Chain Planning
- Serialisation
- (MES) Manufacturing Execution System
- Production Plannning & Scheduling
- Environmental Health & Safety
- (PLM) Product Lifecycle Management
- Quality Management
| COST: |
DEPLOYMENT: |
SCALABILITY: |
| Medium - High |
Cloud or On-Premise |
100 - 10,000+ employees |
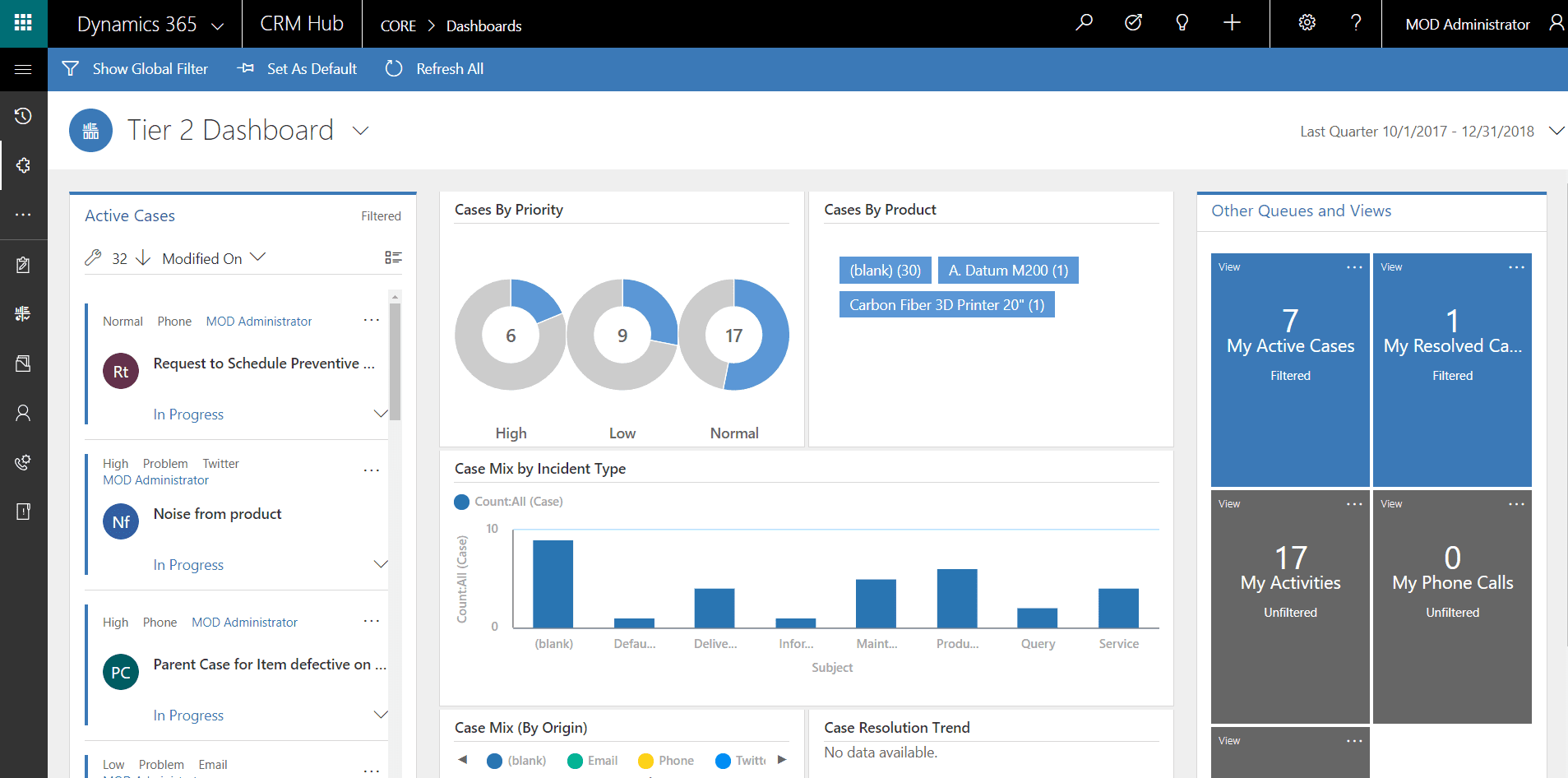
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a fleixble manufacturing ERP that is growing in popularity for medium sized manufacturing businesses in 2024. A key differentiator for D365 is it's integration with the wider Microsoft product suite, from CRM to field service which makes it very robust for manufacturers who need to keep in close, constant contact with their customers.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is only available in a Cloud deployment, which in 2024 is not particularly an issue for most manufacturers, but something to bear in mind.
What manufacturing ERP features does D365 provide?
Dynamics 365 provides ERP capabilities for a number of manufacturing use cases such as process manufacturing, discrete, MTS, MTO, ETO and beyond.
Dynamics 365 provides specific manufacturing ERP capabilities including:
- Master Planning, Capacity Planning, Demand Forecasting, Production Scheduling
- Real-time Production Monitoring, Job Tracking, Work Order Management, Machine Integration
- Inventory Tracking, Warehouse Operations, Lot and Serial Tracking, Quality Control
- Supplier Management, Procurement, Supply Chain Collaboration, Logistics
- Product Data Management, BOM Management, Engineering Change Management
- Costing, Cost Allocation, Budgeting, Profitability Analysis
- Quality Assurance, Nonconformance Management, CAPA, Compliance
- Demand Planning, Sales Forecasting, Business Planning, Collaborative Planning
- Preventive/Predictive Maintenance, Asset Management, Maintenance Scheduling
- Employee Scheduling, Skills Management, Labor Cost Tracking, Safety Management
- Regulatory Compliance, Risk Mitigation, EHS Compliance, Audit Trails
| COST: |
DEPLOYMENT: |
SCALABILITY: |
| Medium |
Cloud |
100 - 1,000 employees |
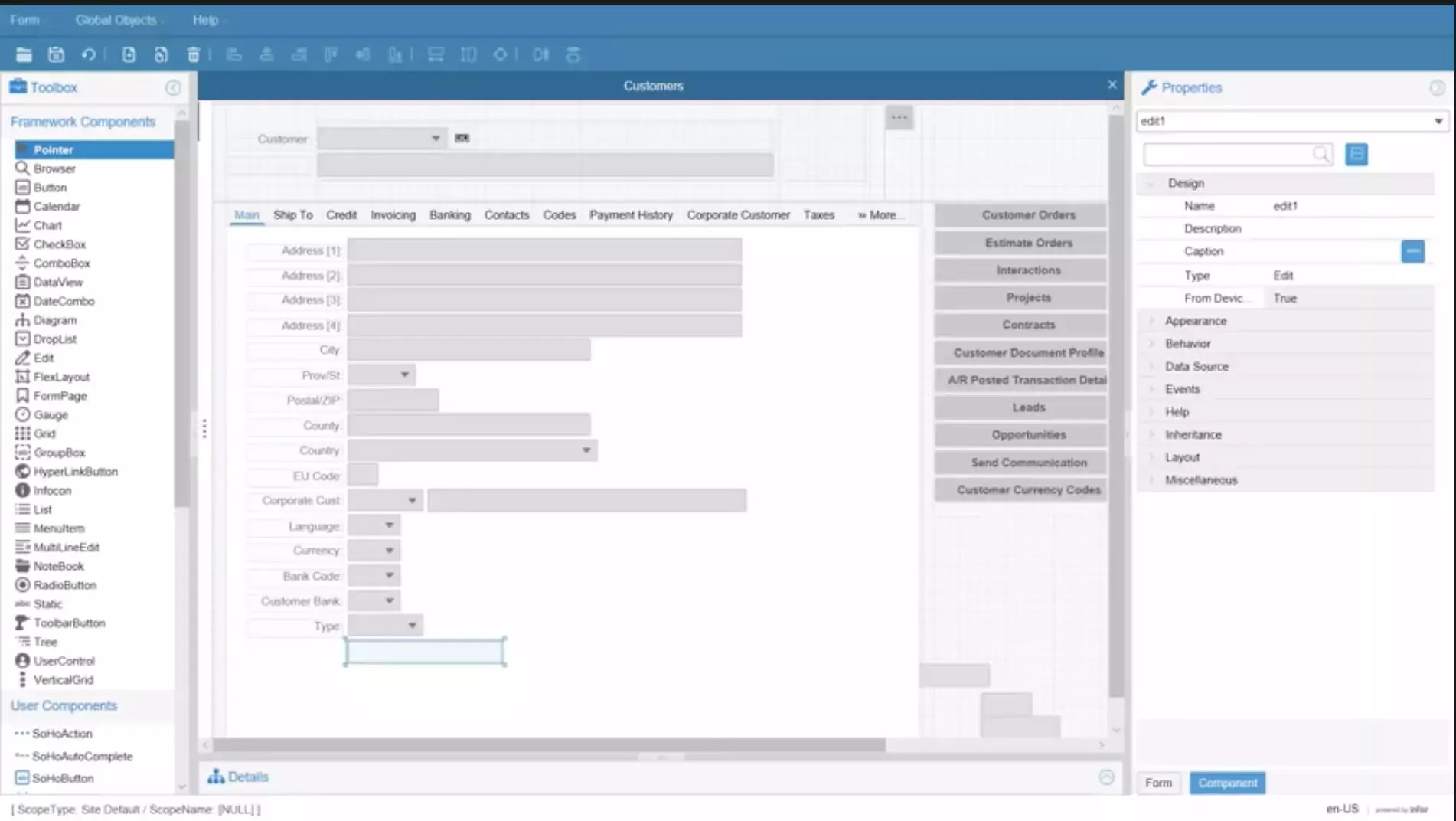
Infor is known for it's industry specialization in ERP systems for the manufacturing industry and Infor CloudSuite Industrial is it's flagship product. Cloudsuite is a great manufacturing ERP for food and beverage manufacturing, industrial manufacturing, discrete and also distribution heavy businesses.
CloudSuite is renowned for it's flexibility and through it's several acquisitions and development over many years, it has a very broad set of functional capabilities.
What manufacturing ERP features does Infor CloudSuite provide?
Infor CloudSuite provides strong capabilities across the entire manufacturing value chain but has particularly strong capabilities in food and beverage, retail and industrial manufacturing ERP.
CloudSuite also provides manufacturing features including:
- Planning, Scheduling, Shop Floor Control, Work Orders
- Supplier, Procurement, Inventory, Logistics
- Product Data, BOM, Engineering Changes
- Quality Control, Nonconformance, CAPA
- Costing, Budgeting, Profitability
- Workforce, Scheduling, Training
- Order Management, After-sales, Warranty
- Real-time Analytics, Dashboards, Custom Reports
- Preventive/Predictive Maintenance, Asset Management
- Regulatory Compliance, Risk Mitigation
| COST: |
DEPLOYMENT: |
SCALABILITY: |
| Medium |
Cloud |
1,000 - 5,000 employees |
Epicor is known for providing manufacturing ERP systems to small and medium sized businesses and it's flagship product is Epicor Kinetic which does exactly that.
Epicor Kinetic offers a range of features that cater to various manufacturing sub-industries and processes, including discrete manufacturing, process manufacturing, and make-to-order operations. From material requirements planning to production scheduling and quality management, Epicor Kinetic ensures seamless operations and enhanced productivity. With a cost-effective deployment model and scalability to accommodate businesses with 100 to 500+ employees, Epicor Kinetic stands out as a top choice for manufacturers.
What manufacturing ERP features does Epicor Kinetic offer?
- Planning, Scheduling, Job Management, Shop Floor Control
- Supplier Management, Inventory, Procurement, Logistics
- Product Data, BOM, PLM, Engineering Changes
- Quality Control, Nonconformance, CAPA
- Costing, Budgeting, Profitability
- Workforce Management, Scheduling, Training
- Order Management, After-sales Support, Warranty
- Real-time Analytics, Dashboards, Custom Reports
- Preventive Maintenance, Asset Management
- Regulatory Compliance, Risk Management
| COST: |
DEPLOYMENT: |
SCALABILITY: |
| Low |
Cloud |
100 to 500+ employees |

Oracle ERP Cloud stands is a powerful tool for manufacturing companies seeking to streamline their operations, although perhaps not as popular in the manufacturing space as solutions like SAP, D365 or Infor CloudSuite. Oracle ERP Cloud offers features tailored to various manufacturing sub-industries and processes. From material requirements planning to supply chain management and quality control.
Oracle is typically associated with larger organisations and is a fit for companies with 500 or more employees.
What manufacturing features does Oracle ERP Cloud offer?
- Planning, Scheduling, Job Management, Shop Floor Control
- Supplier Management, Inventory, Procurement, Logistics
- Product Data, BOM, PLM, Engineering Changes
- Quality Control, Nonconformance, CAPA
- Costing, Budgeting, Profitability
- Workforce Management, Scheduling, Training
- Order Management, After-sales Support, Warranty
- Real-time Analytics, Dashboards, Custom Reports
- Preventive Maintenance, Asset Management
- Regulatory Compliance, Risk Management
| COST: |
DEPLOYMENT: |
SCALABILITY: |
| Medium |
Cloud |
200 - 10,000+ employees |
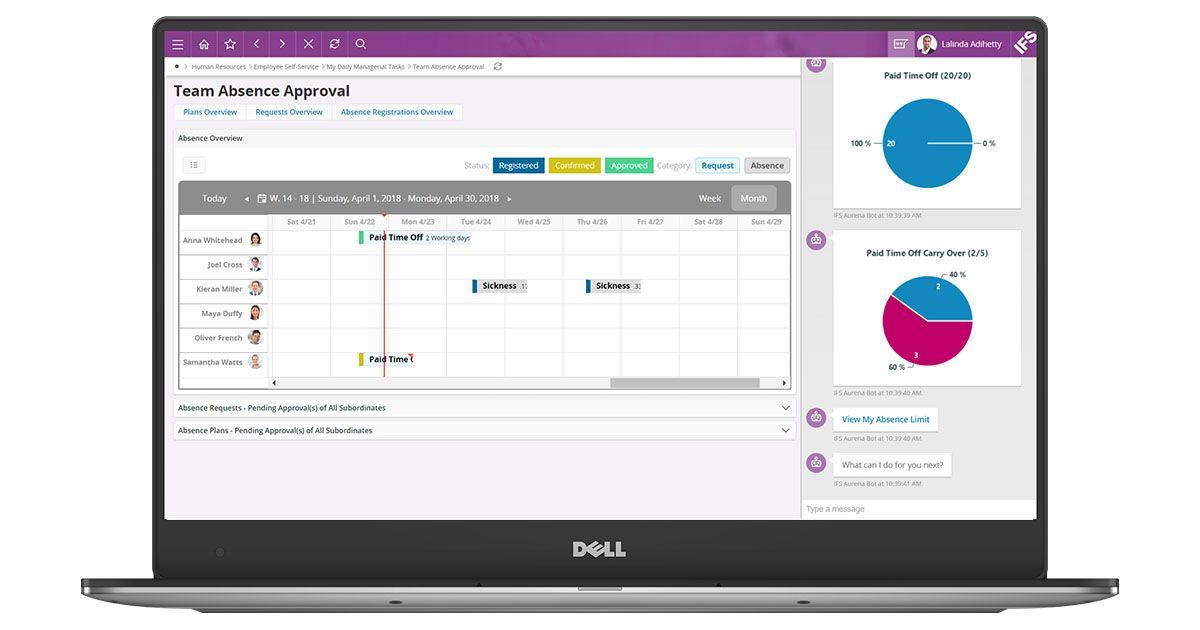
IFS Cloud is another manufacturing ERP that is gaining traction among medium-sized manufacturing businesses in 2024. One of the standout features of IFS Cloud is its ability to offer a truly unified solution that encompasses not just ERP, but also EAM (Enterprise Asset Management), FSM (Field Service Management), and more, making it a versatile choice for manufacturers who need an all-encompassing system.
IFS Cloud is available both as a cloud deployment and an on-premise solution, providing flexibility for manufacturers depending on their infrastructure and data requirements.
What manufacturing ERP features does IFS Cloud provide?
IFS Cloud delivers robust ERP functionalities tailored to various manufacturing environments, including process manufacturing, discrete manufacturing, engineer-to-order (ETO), make-to-stock (MTS), and make-to-order (MTO).
IFS Cloud provides specific manufacturing ERP capabilities including:
- Master Planning, Capacity Planning, Demand Forecasting, Production Scheduling
- Real-time Production Monitoring, Job Tracking, Work Order Management, Machine Integration
- Inventory Tracking, Warehouse Operations, Lot and Serial Tracking, Quality Control
- Supplier Management, Procurement, Supply Chain Collaboration, Logistics
- Product Data Management, BOM Management, Engineering Change Management
- Costing, Cost Allocation, Budgeting, Profitability Analysis
- Quality Assurance, Nonconformance Management, CAPA, Compliance
- Demand Planning, Sales Forecasting, Business Planning, Collaborative Planning
- Preventive/Predictive Maintenance, Asset Management, Maintenance Scheduling
- Employee Scheduling, Skills Management, Labor Cost Tracking, Safety Management
- Regulatory Compliance, Risk Mitigation, EHS Compliance, Audit Trails
| COST: |
DEPLOYMENT: |
SCALABILITY: |
| Medium - High |
Cloud |
500 - 5,000 employees |
.png?width=716&height=386&name=SAP-Business-One-User-Interface%20(UI).png)
SAP Business One is a well-established ERP solution that continues to be a preferred choice for small manufacturing businesses in 2024. O
SAP Business One is available both as an on-premise and cloud solution, allowing manufacturers the flexibility to choose the deployment method that best suits their needs and infrastructure.
What manufacturing ERP features does SAP Business One provide?
SAP Business One offers a comprehensive suite of ERP functionalities designed to support various manufacturing operations, including discrete manufacturing, process manufacturing, and more.
SAP Business One provides specific manufacturing ERP capabilities including:
- Master Planning, Capacity Planning, Demand Forecasting, Production Scheduling
- Real-time Production Monitoring, Job Tracking, Work Order Management, Machine Integration
- Inventory Tracking, Warehouse Operations, Lot and Serial Tracking, Quality Control
- Supplier Management, Procurement, Supply Chain Collaboration, Logistics
- Product Data Management, BOM Management, Engineering Change Management
- Costing, Cost Allocation, Budgeting, Profitability Analysis
- Quality Assurance, Nonconformance Management, CAPA, Compliance
- Demand Planning, Sales Forecasting, Business Planning, Collaborative Planning
- Preventive/Predictive Maintenance, Asset Management, Maintenance Scheduling
- Employee Scheduling, Skills Management, Labor Cost Tracking, Safety Management
| COST: |
DEPLOYMENT: |
SCALABILITY: |
| Low |
On-Premise or Cloud |
50 - 500 employees |

Odoo is an increasingly popular ERP solution among small sized manufacturing businesses in 2024. What sets Odoo apart is its modular approach and open-source nature, which offers manufacturers unparalleled flexibility and customization options. This allows businesses to tailor the ERP system precisely to their unique needs and processes.
Odoo is available both as a cloud-based solution and on-premise, giving manufacturers the flexibility to choose the deployment option that aligns best with their operational and data security requirements.
What manufacturing ERP features does Odoo provide?
Odoo provides a broad range of ERP functionalities that cater to different manufacturing scenarios, including discrete manufacturing, process manufacturing, and custom manufacturing operations.
Odoo provides specific manufacturing ERP capabilities including:
- Master Planning, Capacity Planning, Demand Forecasting, Production Scheduling
- Real-time Production Monitoring, Job Tracking, Work Order Management, Machine Integration
- Inventory Tracking, Warehouse Operations, Lot and Serial Tracking, Quality Control
- Supplier Management, Procurement, Supply Chain Collaboration, Logistics
- Product Data Management, BOM Management, Engineering Change Management
- Costing, Cost Allocation, Budgeting, Profitability Analysis
- Quality Assurance, Nonconformance Management, CAPA, Compliance
- Demand Planning, Sales Forecasting, Business Planning, Collaborative Planning
- Preventive/Predictive Maintenance, Asset Management, Maintenance Scheduling
- Employee Scheduling, Skills Management, Labor Cost Tracking, Safety Management
- Regulatory Compliance, Risk Mitigation, EHS Compliance, Audit Trails
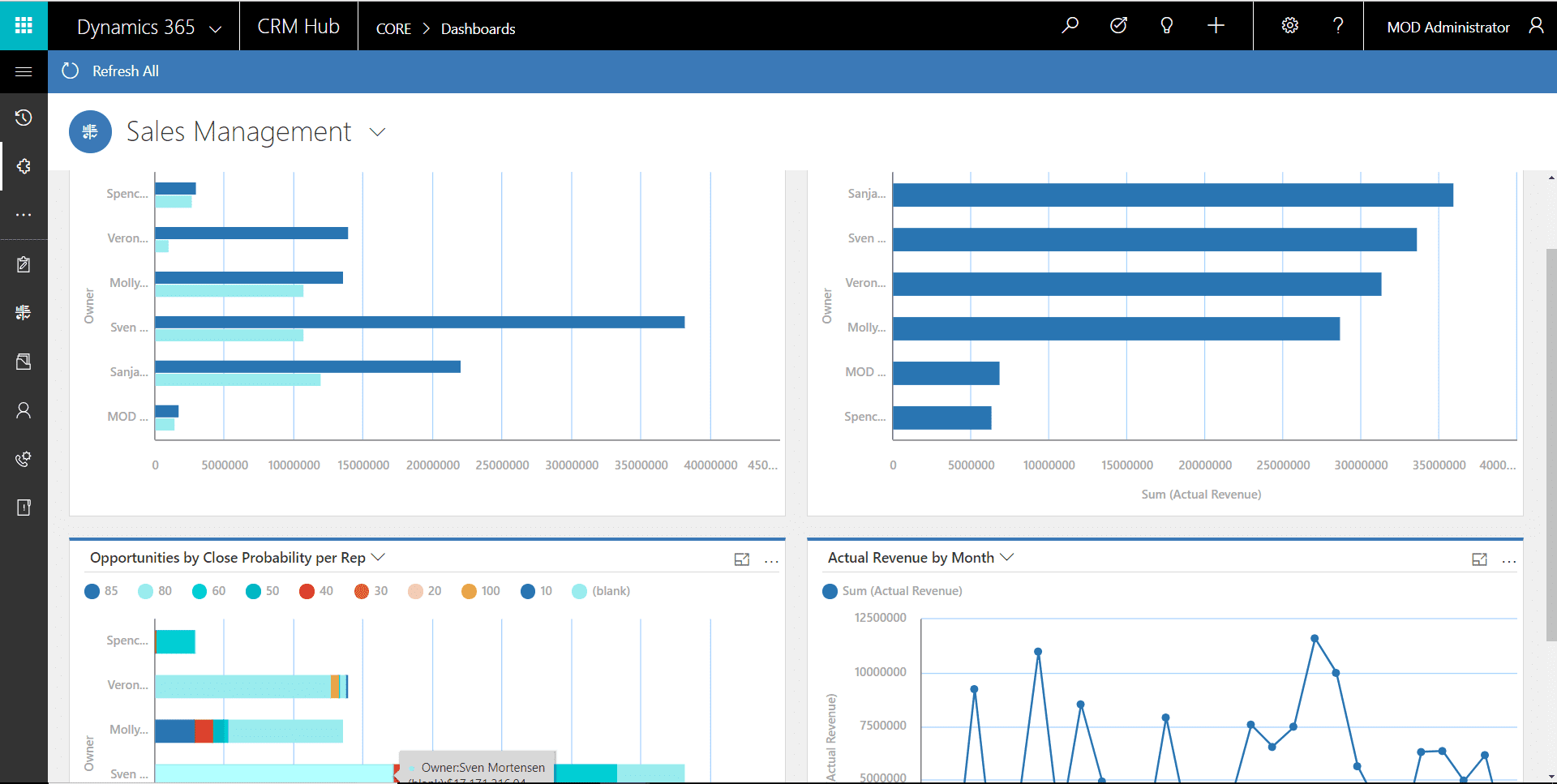
Dynamics 365 Business Central is a robust ERP solution that has been gaining popularity among small to medium-sized manufacturing businesses in 2024. Business Central is the smaller sibling of the larger Dynamics 365 system. A key strength of Business Central is its seamless integration with the broader Microsoft ecosystem, including Office 365 and other Dynamics 365 applications, providing a unified and efficient platform for manufacturers to manage their operations.
Dynamics 365 Business Central is primarily available as a cloud-based solution, although on-premise deployment is also an option, offering flexibility based on a manufacturer’s specific infrastructure and data requirements.
What manufacturing ERP features does Business Central provide?
Business Central delivers a wide array of ERP functionalities tailored to support various manufacturing processes, including discrete manufacturing, process manufacturing, and custom manufacturing.
Dynamics 365 Business Central provides specific manufacturing ERP capabilities including:
- Master Planning, Capacity Planning, Demand Forecasting, Production Scheduling
- Real-time Production Monitoring, Job Tracking, Work Order Management, Machine Integration
- Inventory Tracking, Warehouse Operations, Lot and Serial Tracking, Quality Control
- Supplier Management, Procurement, Supply Chain Collaboration, Logistics
- Product Data Management, BOM Management, Engineering Change Management
- Costing, Cost Allocation, Budgeting, Profitability Analysis
- Quality Assurance, Nonconformance Management, CAPA, Compliance
- Demand Planning, Sales Forecasting, Business Planning, Collaborative Planning
- Preventive/Predictive Maintenance, Asset Management, Maintenance Scheduling
- Employee Scheduling, Skills Management, Labor Cost Tracking, Safety Management
- Regulatory Compliance, Risk Mitigation, EHS Compliance, Audit Trails
| Cost: |
Deployment: |
Scalability: |
| Low |
Cloud or On-Premise |
10 to 500 employees |
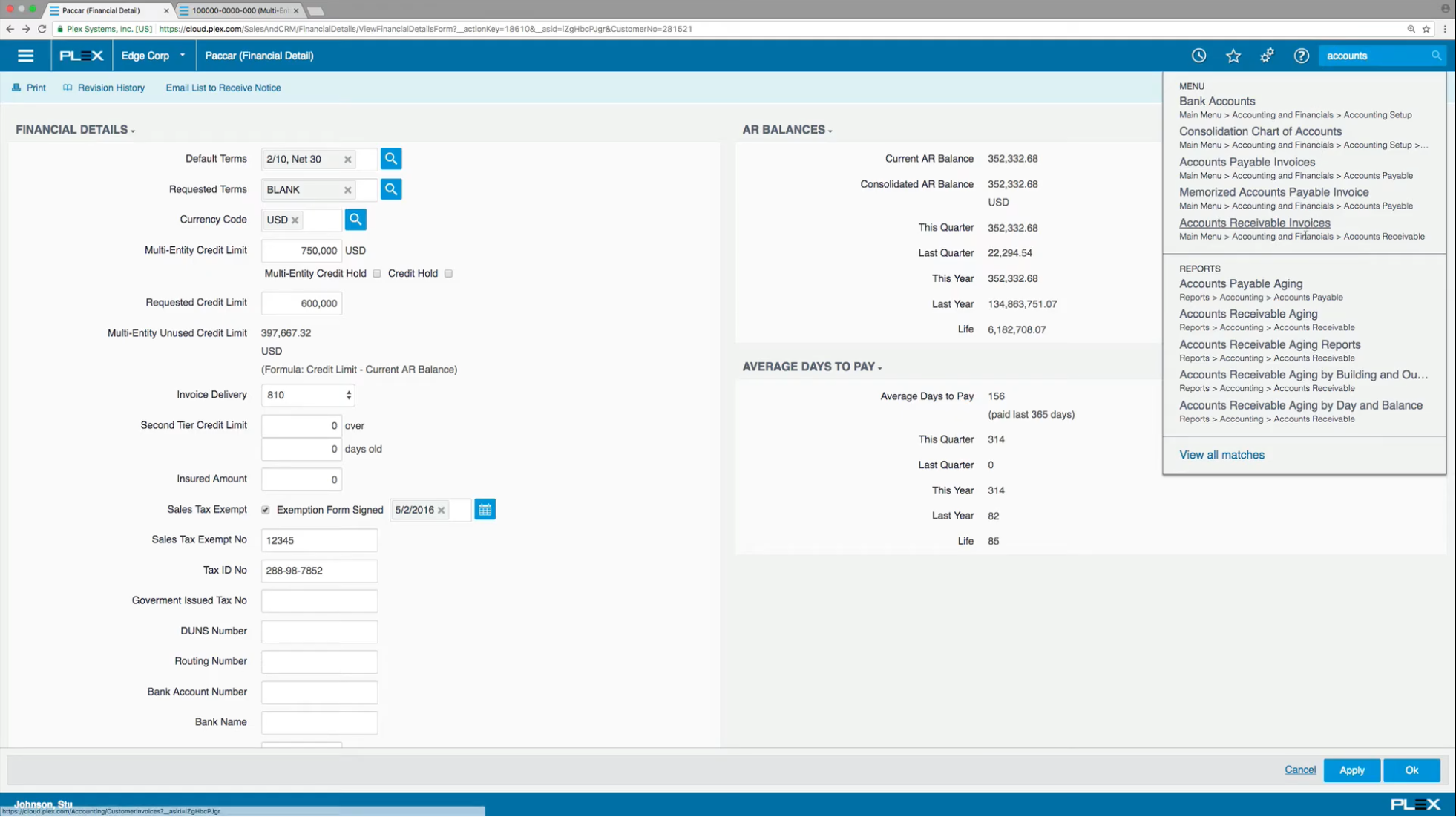
Plex Manufacturing Cloud is an ERP solution that is rapidly becoming a favored choice among medium-sized manufacturing businesses in 2024. One of the primary strengths of Plex Manufacturing Cloud is its focus on the unique needs of manufacturers, providing a comprehensive suite of tools specifically designed for manufacturing operations and industry requirements.
Plex Manufacturing Cloud is exclusively available as a cloud-based solution, which ensures continuous updates, scalability, and accessibility from anywhere, a significant advantage for modern manufacturing businesses.
What manufacturing ERP features does Plex Manufacturing Cloud provide?
Plex Manufacturing Cloud offers extensive ERP functionalities tailored to support various manufacturing operations, including discrete manufacturing, process manufacturing, and custom manufacturing.
Plex Manufacturing Cloud provides specific manufacturing ERP capabilities including:
- Master Planning, Capacity Planning, Demand Forecasting, Production Scheduling
- Real-time Production Monitoring, Job Tracking, Work Order Management, Machine Integration
- Inventory Tracking, Warehouse Operations, Lot and Serial Tracking, Quality Control
- Supplier Management, Procurement, Supply Chain Collaboration, Logistics
- Product Data Management, BOM Management, Engineering Change Management
- Costing, Cost Allocation, Budgeting, Profitability Analysis
- Quality Assurance, Nonconformance Management, CAPA, Compliance
- Demand Planning, Sales Forecasting, Business Planning, Collaborative Planning
- Preventive/Predictive Maintenance, Asset Management, Maintenance Scheduling
- Employee Scheduling, Skills Management, Labor Cost Tracking, Safety Management
- Regulatory Compliance, Risk Mitigation, EHS Compliance, Audit Trails
| Cost: |
Deployment: |
Scalability: |
| Low - Medium |
Cloud |
100 - 500 employees |
What is Manufacturing ERP?
Manufacturing ERP systems centralise business processes and data to help you streamline your operations and optimise your business.
Often, manufacturing businesses run on paper, spreadsheets or lots of siloed systems that don't talk to eachother. Manufacturing ERP systems seek to solve this problem by creating end to end workflows and business processes, which allow you to pass data and process orders, production runs, procurement and more using one integrated system.
An ERP in manufacturing typically covers finance and accounting, production, supply chain management, inventory and warehouse management, sales and beyond, or integrates with other key business applications in these areas to centralise data and create end to end business processes across your different functions.
How do you compare manufacturing ERP?
Comparing ERP systems for manufacturing can take a lot of time and resources from your business, but it's really important to get it right so that you can save time, money and reduce the risk of failure.
You should try to compare ERP systems based on a number of factors including:
Functionality
- Core Modules: Assess the core functionalities such as MRP (Material Requirements Planning), MES (Manufacturing Execution System), quality management, production scheduling, inventory management, and supply chain management.
- Industry-Specific Features: Look for features tailored to specific manufacturing industries (e.g., discrete manufacturing, process manufacturing, make-to-order, engineer-to-order).
- Integration Capabilities: Evaluate how well the ERP integrates with existing systems (e.g., CRM, PLM, SCM) and other third-party applications.
Deployment Options
- Cloud vs. On-Premise: Determine whether the ERP offers cloud-based, on-premise, or hybrid deployment options. Consider factors like data security, IT infrastructure, and scalability.
- Flexibility: Evaluate the flexibility of deployment to see if it aligns with the company’s growth and changes.
Scalability
- User and Transaction Volume: Check if the ERP can scale to accommodate the expected growth in the number of users and transaction volumes.
- Expansion Support: Ensure the ERP supports expansion into new markets or additional production lines or services without requiring significant changes or third party products.
Cost
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the initial licensing or subscription costs, implementation costs, training, maintenance, and any additional fees.
- Value for Money: Compare the features and benefits against the cost to determine overall value for money.
Ease of Use
- User Interface: Evaluate the intuitiveness of the user interface and ease of navigation.
- Learning Curve: Consider the training requirements and how quickly employees can adapt to the new system.
Vendor Support and Reputation
- Customer Support: Assess the quality and availability of customer support, including response times and support channels (e.g., phone, email, live chat).
- Vendor Reputation: Research the vendor’s reputation, including customer reviews, case studies, and industry recognition.
Customization and Flexibility
- Customization Options: Evaluate the ability to customize the ERP to fit specific business processes and needs.
- Modular Design: Consider if the ERP allows adding or removing modules based on changing requirements.
Implementation and Training
- Implementation Time: Assess the estimated time required for implementation and any potential disruptions to operations.
- Training Programs: Evaluate the availability and quality of training programs for employees.
Security and Compliance
- Data Security: Ensure the ERP has robust security features, including data encryption, access controls, and regular security updates.
- Regulatory Compliance: Check if the ERP supports compliance with industry regulations and standards relevant to the business.
Reporting and Analytics
- Reporting Tools: Evaluate the quality and variety of reporting tools and the ability to generate custom reports.
- Real-Time Analytics: Consider the availability of real-time data analytics and dashboards for informed decision-making.
What are the features of a manufacturing ERP?
Lets take a look at the different modules and features that a manufacturing ERP system can provide:
Inventory Management
- Stock control: Helps maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing holding costs and preventing stockouts.
- Warehouse management: Improves warehouse efficiency, reducing picking and packing errors and speeding up order fulfillment.
- Barcode scanning: Enhances accuracy in inventory tracking and speeds up data entry processes.
Production Planning and Control
- Bill of Materials (BOM): Ensures accurate production by listing components and materials needed for manufacturing, reducing errors and waste.
- Master Production Schedule (MPS): Aligns production with demand forecasts to optimize resource use and meet customer deadlines.
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP): Plans material purchases to ensure timely availability, reducing lead times and preventing production delays.
- Capacity Planning: Balances production load with available capacity, ensuring efficient use of resources and avoiding bottlenecks.
Quality Management
- Quality control: Ensures products meet quality standards, reducing returns and increasing customer satisfaction.
- Quality assurance: Implements systematic processes to improve product quality and consistency.
- Compliance management: Ensures adherence to industry regulations and standards, avoiding legal issues and fines.
Supply Chain Management
- Supplier management: Streamlines supplier interactions, improving communication, and fostering better relationships.
- Procurement: Automates purchasing processes, reducing procurement cycle times and costs.
- Order management: Manages customer orders efficiently, ensuring timely delivery and improving customer satisfaction.
- Logistics and distribution: Optimizes transportation and delivery routes, reducing shipping costs and improving delivery times.
Sales and Distribution
- Sales order processing: Automates order entry and processing, reducing errors and speeding up the sales cycle.
- Pricing and discounts: Manages pricing strategies and discount structures, enhancing sales performance.
- Customer relationship management (CRM): Tracks customer interactions, improving customer service and retention.
Finance and Accounting
- General ledger: Provides a central repository for financial data, ensuring accurate financial reporting.
- Accounts payable and receivable: Automates invoicing and payment processes, improving cash flow management.
- Fixed asset management: Tracks assets, schedules maintenance, and calculates depreciation, optimizing asset utilization.
- Budgeting and forecasting: Helps plan and control financial resources, improving financial stability and planning.
Human Resources Management
- Employee records: Centralizes employee information, facilitating efficient HR management.
- Payroll: Automates payroll processing, ensuring timely and accurate employee payments.
- Time and attendance: Tracks employee work hours, reducing time theft and improving productivity.
- Recruitment and onboarding: Streamlines hiring processes, ensuring the right talent is onboarded quickly.
Maintenance Management
- Equipment maintenance: Schedules and tracks maintenance activities, reducing downtime and extending equipment life.
- Preventive maintenance scheduling: Prevents equipment failures through regular maintenance, improving reliability.
- Work order management: Manages maintenance requests and work orders efficiently, ensuring timely resolution.
Project Management
- Project planning: Facilitates detailed project planning, improving project execution and delivery.
- Resource allocation: Optimizes resource use, ensuring projects are completed on time and within budget.
- Project costing: Tracks project expenses, providing insights into project profitability.
- Time tracking: Monitors project timelines, helping to keep projects on schedule.
How do you compare manufacturing ERP systems?
How much does manufacturing ERP cost?
Implementing an ERP in a manufacturing business comes with a lot of different costs and the first year investment can take anything from $50,000 to several millions, if not dozens of millions of dollars.
It's important to start you manufacturing ERP project by identifying the different costs that crop up throughout the process and trying to quantify how much it will cost for your business.
Here's a breakdown of the different costs:
Software Licensing
-
- ERP Software License: The cost varies depending on the size of the organization, the number of users, and the ERP vendor. Typical costs can range from $1,000 to $5,000 per user, per year for cloud-based solutions. For on-premises solutions, it might be a one-time fee ranging from $50,000 to $500,000 or more.
- Additional Modules: Some modules might not be included in the base package and could cost extra. Prices can range from $5,000 to $50,000 per module.
Hardware Costs
-
- Servers: If opting for an on-premises solution, servers and related hardware can cost between $10,000 and $100,000.
- Network Infrastructure: Upgrading network infrastructure to support the ERP system might cost between $5,000 and $50,000.
- Workstations and Devices: New or upgraded computers, barcode scanners, and other devices may be needed, costing between $500 and $2,000 per device.
Implementation Services
Consultation and Planning: Consulting fees for project planning and analysis can range from $10,000 to $100,000 depending on the complexity of the project.
Customization: Customizing the ERP to fit specific business needs can cost between $20,000 and $200,000 or more.
Integration: Integrating the ERP with existing systems and data migration can cost between $10,000 and $100,000.
Testing and Quality Assurance: Ensuring the system works correctly and is bug-free might cost between $5,000 and $50,000.
Training and Support
-
- Training: Training employees on the new system can cost between $1,000 and $5,000 per user.
- Support and Maintenance: Annual support and maintenance fees typically range from 15% to 20% of the initial software license cost.
How long does it take to implement manufacturing ERP?
Implementing any ERP system can take anywhere from a few months, through to several years. The length of time it takes to implement an ERP system depends on a number of factors. You should try to gauge how your organisation fits into these different parameters so you can understand how long it will take to implement your chosen ERP system.
These factors include:
Size of the Organization
Larger organizations with more complex structures and processes typically require more time for implementation.
Complexity of Business Processes
Businesses with highly specialized or complex processes may need extensive customization and integration, extending the implementation timeline.
Scope of the ERP Solution
The number of modules being implemented and the extent of integration with other systems can significantly impact the timeline.
Level of Customization
Extensive customization to meet specific business needs can add considerable time to the project.
Data Quality and Volume
The quality and volume of data to be migrated can influence the time required for data preparation and migration.
User Readiness and Change Management
The readiness of the organization to adopt the new system and the effectiveness of change management strategies can affect the implementation timeline.
Vendor and Implementation Partner
The experience and efficiency of the ERP vendor and implementation partner play a critical role in the speed and success of the project.
Should you choose a Cloud or On-Premise Manufacturing ERP?
There are many advantages and disadvantages with both Cloud and On-Premise ERP systems, however the market is undeniably moving to Cloud ERP as the defacto way of deploying a new ERP system.
What are different stages of implementing a manufacturing ERP?
ERP system implementations go through several different gates before, and after go-live. Here's a breakdown of the different steps involved:
Project Planning and Preparation (1-3 months)
Needs Analysis: Assessing business needs, defining objectives, and determining the scope of the ERP project.
Vendor Selection: Researching and selecting the appropriate ERP vendor and software solution.
Project Team Formation: Assembling a project team that includes representatives from key departments, IT staff, and external consultants if necessary.
System Design and Customization (2-6 months)
Requirements Gathering: Detailed documentation of business processes, requirements, and workflows.
Gap Analysis: Identifying gaps between the ERP system's capabilities and business requirements.
Customization: Configuring and customizing the ERP software to meet specific business needs, which can vary widely in time based on the level of customization required.
Data Migration (2-4 months)
Data Cleaning: Preparing and cleaning existing data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Data Mapping: Defining how existing data will be migrated into the new ERP system.
Data Transfer: Executing the data migration process and validating the integrity of the transferred data.
Integration (2-4 months)
System Integration: Integrating the ERP system with existing applications and third-party systems such as CRM, supply chain management, and e-commerce platforms.
Interface Development: Developing and testing interfaces between the ERP and other systems to ensure seamless data flow.
Testing and Quality Assurance (3-6 months)
Unit Testing: Testing individual components of the ERP system to ensure they function correctly.
Integration Testing: Ensuring that different modules and integrations work together as intended.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Engaging end-users to test the system in real-world scenarios to identify any issues or gaps.
Training (1-3 months)
Training Plan: Developing a comprehensive training plan to ensure all users are adequately trained.
Training Sessions: Conducting training sessions for different user groups, including end-users, IT staff, and managers.
Documentation: Providing user manuals, quick reference guides, and other training materials.
Deployment (1-2 months)
Pilot Deployment: Implementing the ERP system in a limited scope (e.g., a single department or location) to identify and resolve any issues.
Full Deployment: Rolling out the ERP system across the entire organization.
Benefits of Manufacturing ERP
Implementing an ERP system for your manufacturing system comes with a whole host of benefits. Centralising data and processes can make your business more efficient, competitive, customer centric, sustainable and beyond.
Here's a full breakdown of the benefits of implementing an ERP system in your manufacturing business:
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
- Automated Processes: Automating routine tasks reduces manual effort and the likelihood of errors, leading to faster and more efficient operations.
- Streamlined Operations: Integrating various functions (e.g., procurement, production, sales) into a single system streamlines workflows and improves coordination among departments.
Enhanced Data Accuracy and Reporting
- Real-time Data: Access to real-time data allows for better decision-making and quicker response to changes in demand, supply chain issues, or production problems.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Advanced reporting tools provide insights into various aspects of the business, helping in performance monitoring and strategic planning.
Cost Reduction
- Inventory Management: Optimized inventory levels reduce carrying costs and minimize stockouts or overstock situations.
- Production Planning: Efficient production scheduling and resource allocation reduce waste and operational costs.
Better Quality Control
- Quality Management: ERP systems include quality management modules that ensure products meet required standards and reduce the rate of defects and rework.
- Traceability: Enhanced traceability features help track the origin of materials and the path of finished products, which is crucial for quality control and regulatory compliance.
Improved Supply Chain Management
- Supplier Collaboration: Improved communication and collaboration with suppliers lead to better procurement practices and more reliable supply chains.
- Demand Forecasting: Accurate demand forecasting helps align production schedules with market demands, reducing lead times and improving customer satisfaction.
Scalability
- Support for Growth: ERP systems can scale with the growth of the business, accommodating increasing transaction volumes and expanding operations without significant changes to the system infrastructure.
Regulatory Compliance
- Compliance Management: ERP systems help ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards by providing necessary documentation and audit trails.
- EHS Management: Modules for Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) ensure that the manufacturing processes adhere to environmental regulations and safety standards.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
- Improved Order Management: Better order tracking and fulfillment processes lead to faster deliveries and improved customer service.
- Personalized Service: Detailed customer data helps in providing personalized service and building stronger customer relationships.
Workforce Management
- Employee Scheduling: Efficient workforce scheduling and management ensure that the right number of skilled employees are available when needed.
- Labor Cost Tracking: Tracking labor costs helps in managing payroll and reducing unnecessary labor expenses.
Innovation and Continuous Improvement
- Support for R&D: ERP systems provide tools for managing research and development (R&D) activities, facilitating innovation and continuous improvement in products and processes.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Access to comprehensive data supports a culture of data-driven decision-making, fostering continuous improvement.





.png?width=716&height=386&name=SAP-Business-One-User-Interface%20(UI).png)


