Workday VS SAP - Independent Comparison
Read our independent guide to SAP vs Workday, the pros, cons and functionality. Understand the difference between S/4, SuccessFactors and Workday.
SAP Vs Microsoft Dynamics. Two titans of business and enterprise software for both ERP, CRM and beyond. In this guide ...
SAP Vs Microsoft Dynamics. Two titans of business and enterprise software for both ERP, CRM and beyond. In this guide we'll perform an independent comparison of each solution and find out which one is the winner.
The user experience (UX) of an ERP system is crucial as it directly impacts user adoption, productivity, and satisfaction. Both SAP S/4HANA and Microsoft Dynamics have made significant strides in improving their UX to meet the evolving needs of modern users. Here's a comparison of the user experience offered by both platforms:
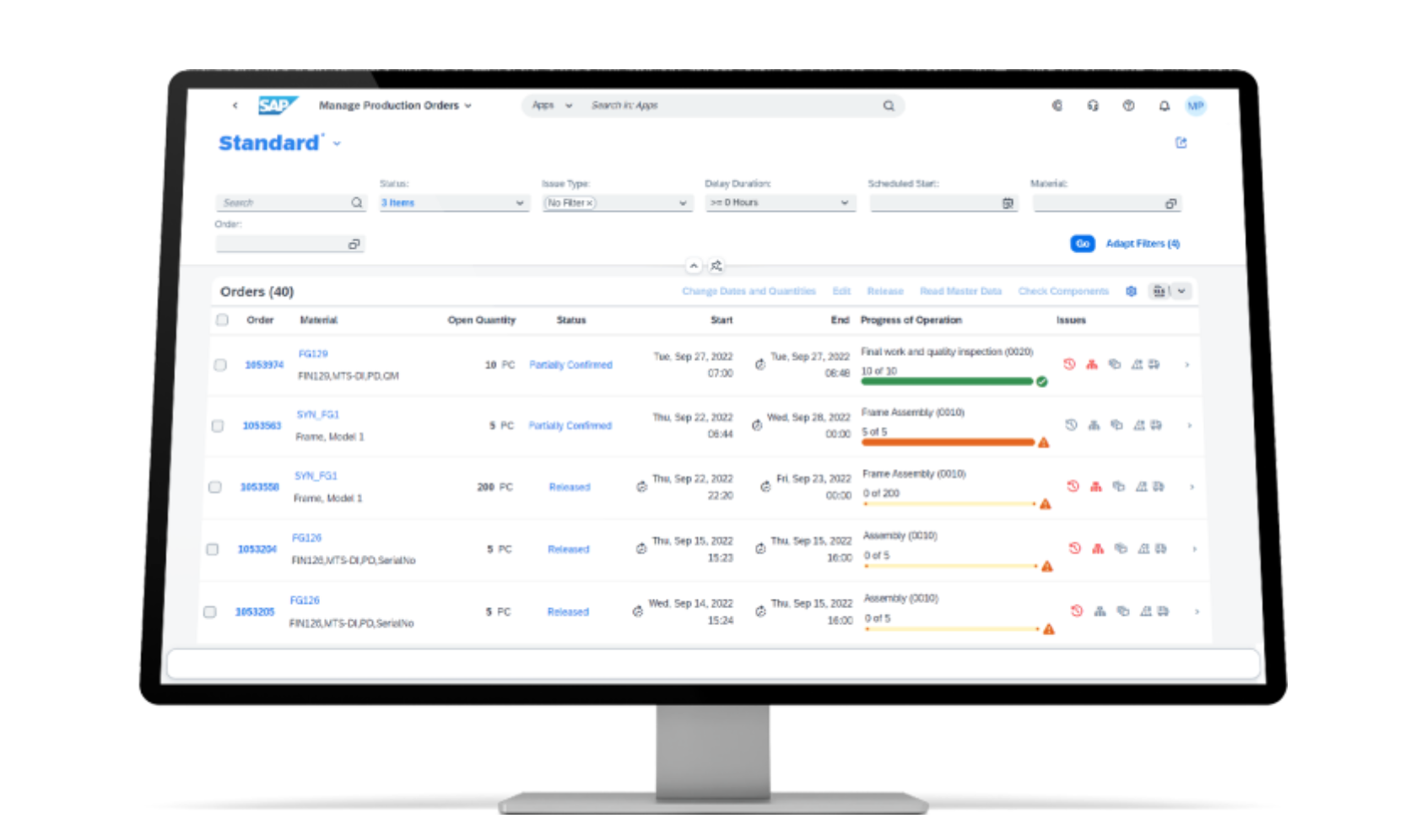
Fiori UX: SAP S/4HANA leverages the SAP Fiori UX, which represents a major shift from traditional SAP GUI interfaces. Fiori provides a modern, role-based UX design that is consistent across all devices (desktop, tablet, and mobile). This approach aims to enhance productivity by simplifying the user interface (UI) and focusing on the most critical tasks and information for each role.
Personalization: Users can personalize their Fiori launchpad by adding or removing tiles (apps) based on their preferences and job functions. This level of personalization ensures that users have quick access to the tools and information they use most frequently.
Integration of Analytics: SAP S/4HANA integrates analytics directly into the user interface, allowing users to make data-driven decisions in real-time without leaving the application. This seamless integration of analytics into business processes enhances the decision-making capabilities of users.
Learning Curve: The transition to Fiori from traditional SAP GUI can require a significant learning curve for users accustomed to the older interfaces. However, SAP provides extensive training resources and tools to support this transition.
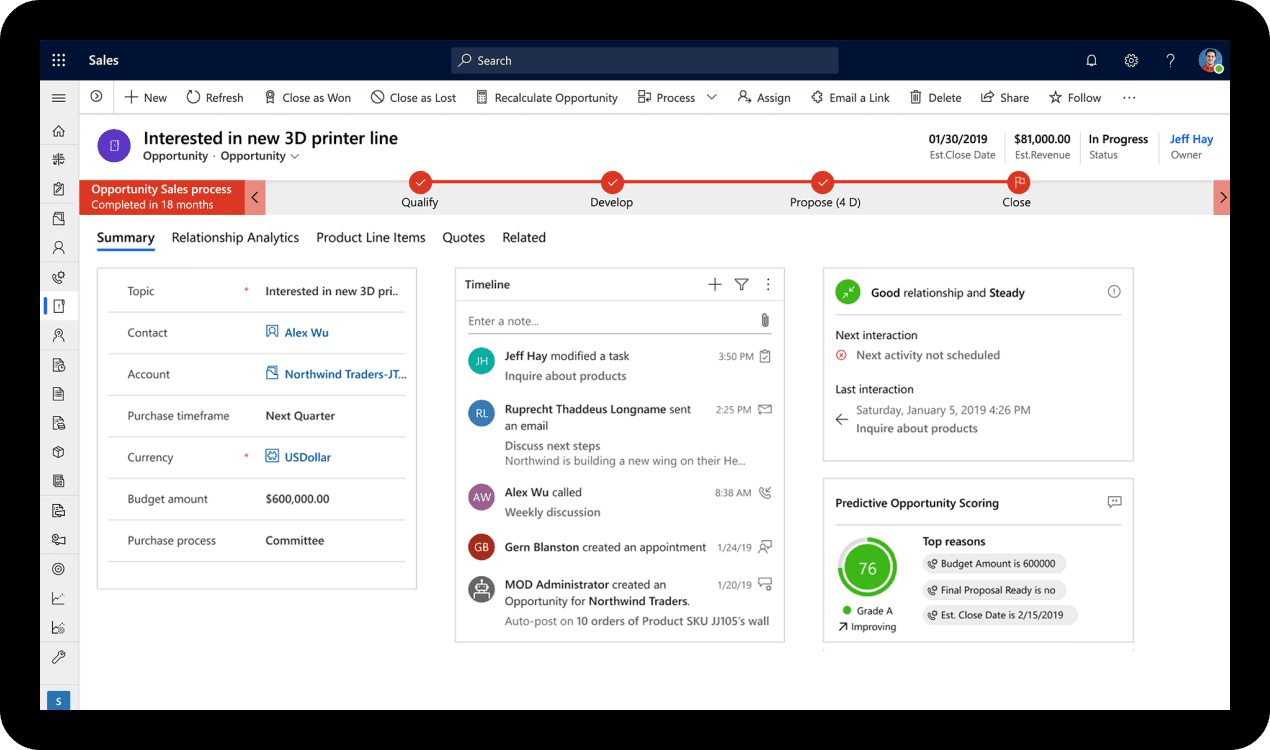
Unified Interface: Microsoft Dynamics uses a Unified Interface across its Dynamics 365 applications, providing a consistent and responsive experience across devices. This interface focuses on simplicity and efficiency, with an emphasis on clean layouts and ease of navigation.
Integration with Microsoft Products: Dynamics offers deep integration with other Microsoft products such as Office 365, Outlook, and Teams. This integration facilitates a smoother workflow, allowing users to perform ERP tasks directly from familiar tools like Outlook or Teams, significantly enhancing productivity and user adoption.
Customization and Flexibility: Microsoft Dynamics provides a high degree of customization and flexibility in its user interface. Users can easily configure views, forms, and dashboards without needing deep technical skills. The Power Platform (Power BI, Power Apps, and Power Automate) further extends this flexibility, enabling users to create custom apps and workflows.
Ease of Use: Generally, users find Microsoft Dynamics to be intuitive, especially those already familiar with the Microsoft ecosystem. The learning curve is often perceived to be lower than that for SAP S/4HANA, particularly for users who regularly use other Microsoft products.
SAP S/4HANA is a next-generation enterprise resource planning (ERP) suite designed by SAP to provide businesses with a highly efficient, real-time, and integrated ERP solution. It is built on SAP's advanced in-memory platform, SAP HANA, and offers a personalized user experience with SAP Fiori. Below is a detailed summary of its functionality across various modules and areas:
Microsoft Dynamics is a line of enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM) software applications designed to help businesses manage their operations, customer interactions, and financial processes more efficiently. The Dynamics suite includes several primary products, each catering to different business needs and sizes. Below is a detailed summary of the functionality provided by the major Microsoft Dynamics products:
SAP S/4HANA is highly regarded in the manufacturing industry for its robust capabilities in supply chain management, production planning, and operational excellence. Its ability to handle complex manufacturing processes, integrate with IoT devices for real-time data analysis, and support for lean manufacturing make it a strong fit for large manufacturing firms with complex operations.
Microsoft Dynamics offers strong manufacturing capabilities with Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management, focusing on streamlining operations, optimizing resource planning, and improving product delivery. Its flexibility and ease of customization make it suitable for mid-sized to large manufacturers, especially those looking for a solution that can be tailored to unique processes.
SAP S/4HANA provides comprehensive support for the retail industry, including omnichannel commerce, customer experience management, and inventory management. Its strength lies in handling large volumes of transactions and data analytics, making it ideal for large retailers with complex supply chains and a global presence.
Microsoft Dynamics excels in the retail sector with Dynamics 365 Commerce, offering a unified commerce platform that enables personalized customer engagement, efficient operations, and adaptable retail processes. It is well-suited for mid-sized to large retail operations that prioritize customer experience and need a flexible, integrated retail solution.
SAP S/4HANA is capable of supporting the healthcare industry with its powerful analytics, patient care management, and financial tools. Its ability to integrate with specialized healthcare applications and compliance with healthcare regulations makes it a viable option for large healthcare providers needing comprehensive ERP capabilities with a focus on patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Microsoft Dynamics offers a tailored approach to healthcare through Dynamics 365 Healthcare and its integration capabilities with Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare. It provides tools for patient engagement, health team collaboration, and operational insights, making it suitable for healthcare organizations of all sizes looking for a flexible, interoperable platform that can adapt to changing healthcare needs.
SAP S/4HANA is highly favored in the finance sector for its strong financial management, risk analysis, and regulatory compliance features. It offers deep functionality for financial operations, real-time analytics, and treasury management, making it a good fit for large financial institutions requiring robust, global financial management capabilities.
Microsoft Dynamics supports the finance industry with Dynamics 365 Finance, delivering comprehensive financial reporting, AI-driven insights, and automation of financial operations. It is suited for financial services firms of all sizes that need a flexible, scalable solution for managing finances, risk, and compliance in a rapidly changing environment.
SAP S/4HANA offers specialized solutions for the public sector, including capabilities for public finance management, procurement, and citizen services. Its ability to support large-scale operations and comply with government regulations makes it suitable for government agencies and public institutions seeking an integrated ERP solution to improve efficiency and public value.
Microsoft Dynamics provides tailored solutions for the public sector with Dynamics 365, focusing on government and public services. It offers tools for case management, regulatory compliance, and citizen engagement. Its modular approach and flexibility make it appropriate for public sector organizations of various sizes looking for a solution to modernize operations and enhance service delivery.
The implementation process of an ERP system is critical to its success and long-term value to an organization. Both SAP S/4HANA and Microsoft Dynamics offer comprehensive ERP solutions, but their implementation processes can differ significantly due to their distinct architectures, target markets, and deployment options. Here's a comparison of the implementation processes for SAP S/4HANA and Microsoft Dynamics:
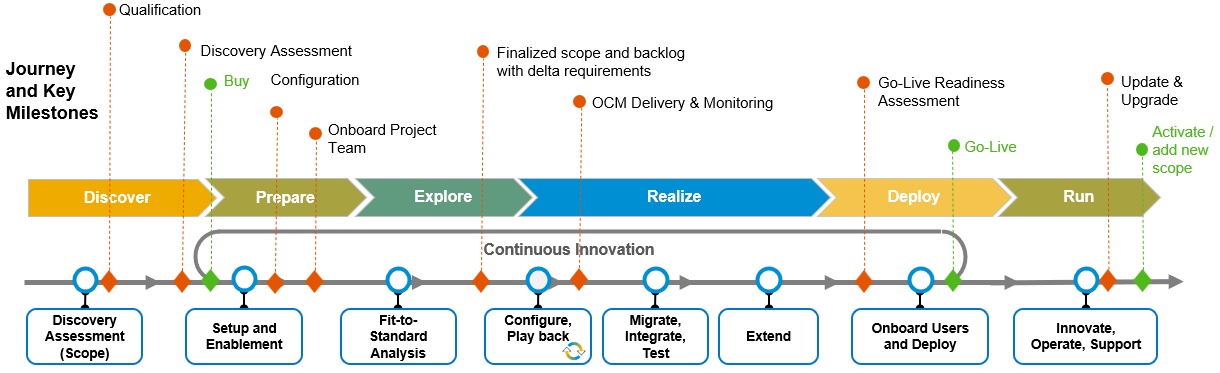
The histories of SAP S/4HANA and Microsoft Dynamics reflect their evolution in addressing the changing needs of businesses in the realm of enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM). Both have grown from their initial offerings to become leaders in the ERP and CRM markets, albeit with different origins and development paths. Here's a comparison of their historical developments:

Origins: SAP, founded in 1972, has a long history in the ERP market, beginning with its R/2 system in the 1970s, evolving to R/3 in the 1990s, and then to SAP ERP (ECC) in the early 2000s. These systems laid the groundwork for integrated business applications.
Launch of S/4HANA: SAP S/4HANA was officially launched in February 2015 as a next-generation ERP system, designed to address the complexities and demands of the digital economy. It was built from the ground up to utilize the advanced in-memory database technology of SAP HANA, offering enhanced performance, real-time analytics, and simplified processes.
Evolution: Since its launch, SAP S/4HANA has undergone continuous development, with SAP releasing updates and enhancements to expand its capabilities, including cloud offerings (SAP S/4HANA Cloud) and industry-specific solutions. The focus has been on leveraging the power of HANA's in-memory computing, improving user experience with Fiori, and enhancing the system's ability to integrate with new technologies and external systems.
Migration Push: SAP has actively encouraged its existing customers to migrate from SAP ECC to S/4HANA, setting initial deadlines (now extended) for the end of maintenance for ECC, to transition users to the more advanced S/4HANA platform.
Origins: Microsoft entered the ERP market through acquisitions in the early 2000s. Key acquisitions included Great Plains Software in 2001 and Navision A/S in 2002, which later evolved into Dynamics GP and Dynamics NAV, respectively. These acquisitions laid the foundation for Microsoft's entry into business applications.
Dynamics Brand Launch: In 2003, Microsoft consolidated its business applications under the Dynamics brand. Over the years, this included Dynamics AX (originally Axapta), Dynamics NAV (Navision), Dynamics GP (Great Plains), Dynamics SL (Solomon), and eventually Dynamics CRM.
Dynamics 365 Introduction: In 2016, Microsoft launched Dynamics 365, a cloud-based suite of ERP and CRM applications. This represented a significant shift towards integrating ERP and CRM capabilities with the broader Microsoft ecosystem, including Office 365, Azure, and Power Platform, to offer a unified business solution platform.
Continuous Evolution: Microsoft Dynamics 365 has continuously evolved, adding new applications (e.g., Dynamics 365 Sales, Dynamics 365 Customer Service, Dynamics 365 Finance) and capabilities to support digital transformation. Microsoft has focused on cloud-first solutions, AI, and data analytics integration, enhancing the platform's usability and scalability.
License Model: SAP S/4HANA offers both on-premise and cloud (public and private) deployment options. The pricing for on-premise versions typically involves a one-time perpetual license fee based on the number of users and the scope of functionality required. Cloud versions are generally offered on a subscription basis, with costs depending on the number of users, processes, and data volume.
Implementation Costs: The implementation costs for SAP S/4HANA can be substantial, especially for large, global enterprises requiring extensive customization and integration with existing systems. Implementation involves not just the cost of external consultants and system integrators but also internal resources for project management, training, and change management.
Customization and Integration: Customizing SAP S/4HANA to fit specific business processes and integrating it with other systems can add significant costs. The complexity of the business processes and the extent of customization required will heavily influence these costs.
Maintenance and Support: SAP typically charges an annual maintenance fee for on-premise deployments, which is a percentage of the software license fee. For cloud versions, support and maintenance costs are included in the subscription fee.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): The TCO for SAP S/4HANA can be high, particularly for large, complex implementations. However, it's designed to offer significant value through efficiency gains, real-time insights, and improved decision-making capabilities.
License Model: Microsoft Dynamics 365 is primarily offered as a cloud-based solution with a subscription pricing model. The costs are based on a per-user, per-month basis, with different plans available depending on the applications and functionalities needed. Dynamics 365 also offers flexibility to mix and match apps to suit specific business requirements.
Implementation Costs: Implementation costs for Dynamics 365 can vary widely. Smaller implementations and businesses with less complex needs may find the costs to be lower than those for SAP S/4HANA, particularly due to the availability of pre-configured solutions and integrations within the Microsoft ecosystem. However, larger, more customized implementations can still be costly.
Customization and Integration: Dynamics 365 allows for a significant degree of customization and integration, especially with other Microsoft products like Office 365 and Azure. While this can reduce some integration costs, extensive customizations can increase overall project costs.
Maintenance and Support: For the cloud-based subscription, maintenance, updates, and support are included in the monthly subscription fee. This can simplify budgeting and reduce unexpected costs compared to traditional on-premise solutions.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): The TCO for Microsoft Dynamics 365 can be more predictable than for SAP S/4HANA, particularly for small to medium-sized businesses. However, large-scale deployments with extensive customizations can also result in significant costs.
Read our independent guide to SAP vs Workday, the pros, cons and functionality. Understand the difference between S/4, SuccessFactors and Workday.
We explore SAP S/4 HANA Public Cloud in our independent guide, covering the costs, functionality and suitability of the solution in various different...
Learn how to kick off an SAP S/4 HANA ERP implementation project independently. Understand the flavours of S/4 HANA, best practices and partners.
SAP S/4 HANA vs Oracle ERP Cloud. We compare two of the worlds largest ERP vendors across functionality, industry fit, history, implementation and...
In our independent guide to SAP S/4 HANA Private Cloud (PCE), we explore the service offering, pros and cons, costs and more.
Read out guide to completing an SAP carve out, divestiture or SAP divestment and understand the implications of target ERP systems like SAP S/4 HANA.
Be the first to know about new B2B SaaS Marketing insights to build or refine your marketing function with the tools and knowledge of today’s industry.